Winter Sowing in Zone 6: A Complete Calendar and Information
Associated Articles: Winter Sowing in Zone 6: A Complete Calendar and Information
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Winter Sowing in Zone 6: A Complete Calendar and Information. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Winter Sowing in Zone 6: A Complete Calendar and Information

Zone 6 gardeners take pleasure in an extended rising season than many, however winter’s chill nonetheless dictates the planting schedule. Winter sowing, the artwork of beginning seeds outdoor in recycled containers over winter, gives a intelligent option to bypass the necessity for indoor seed beginning, saving area, time, and assets. This system permits nature to do the work, regularly warming and moistening the seeds as spring arrives. This text supplies an in depth Zone 6 winter sowing calendar, together with important ideas and concerns for achievement.
Understanding Zone 6 and its Microclimates:
USDA Plant Hardiness Zone 6 experiences common annual minimal temperatures between -10°F and 0°F (-23°C and -18°C). Nevertheless, microclimates inside Zone 6 can fluctuate considerably. North-facing slopes are typically colder and shadier, whereas south-facing slopes are hotter and sunnier. Location inside your backyard, proximity to buildings, and wind publicity all affect temperatures. Observing your personal backyard’s microclimates is essential for optimum winter sowing success. A thermometer positioned close to your winter sowing containers will present useful knowledge.
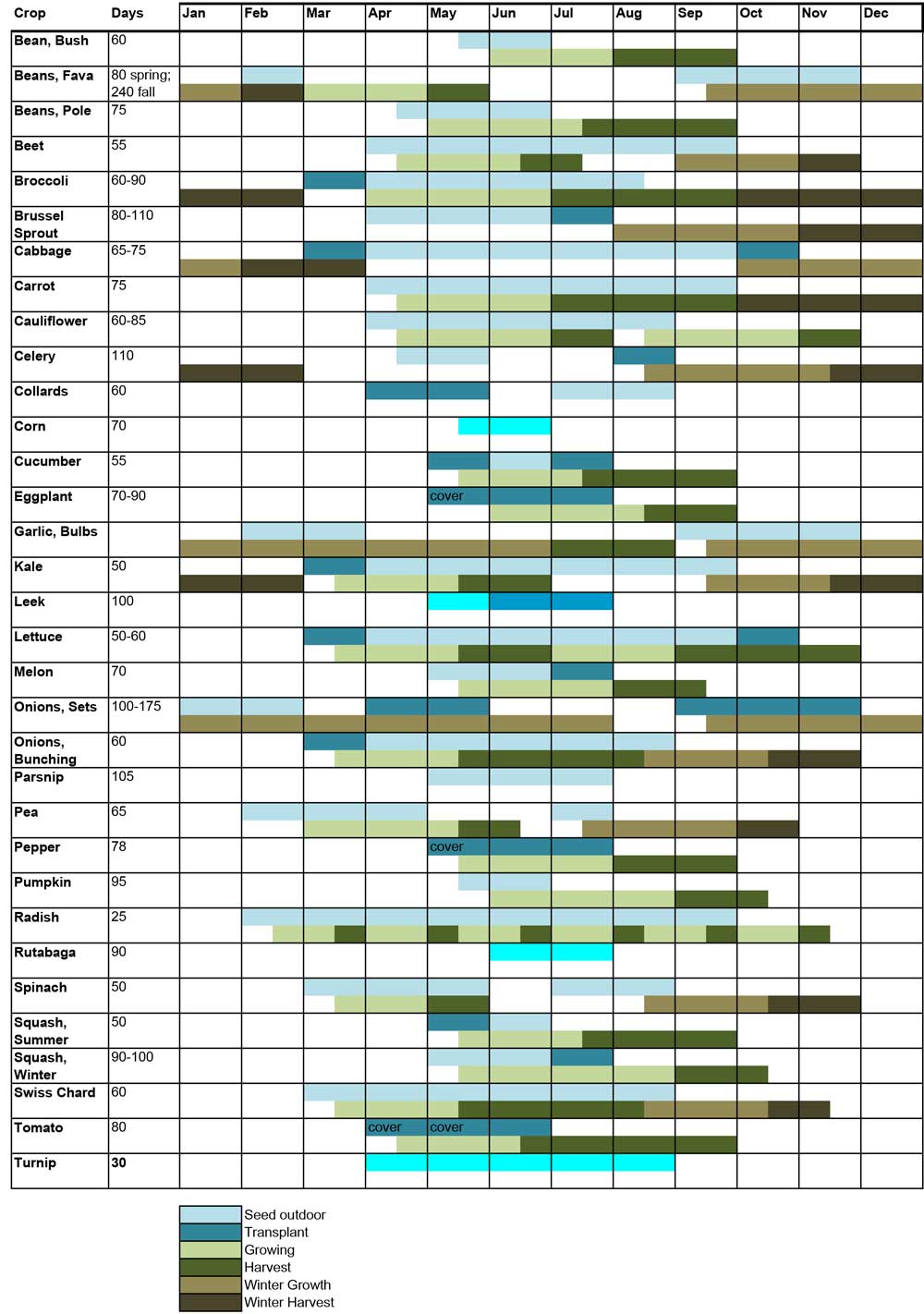
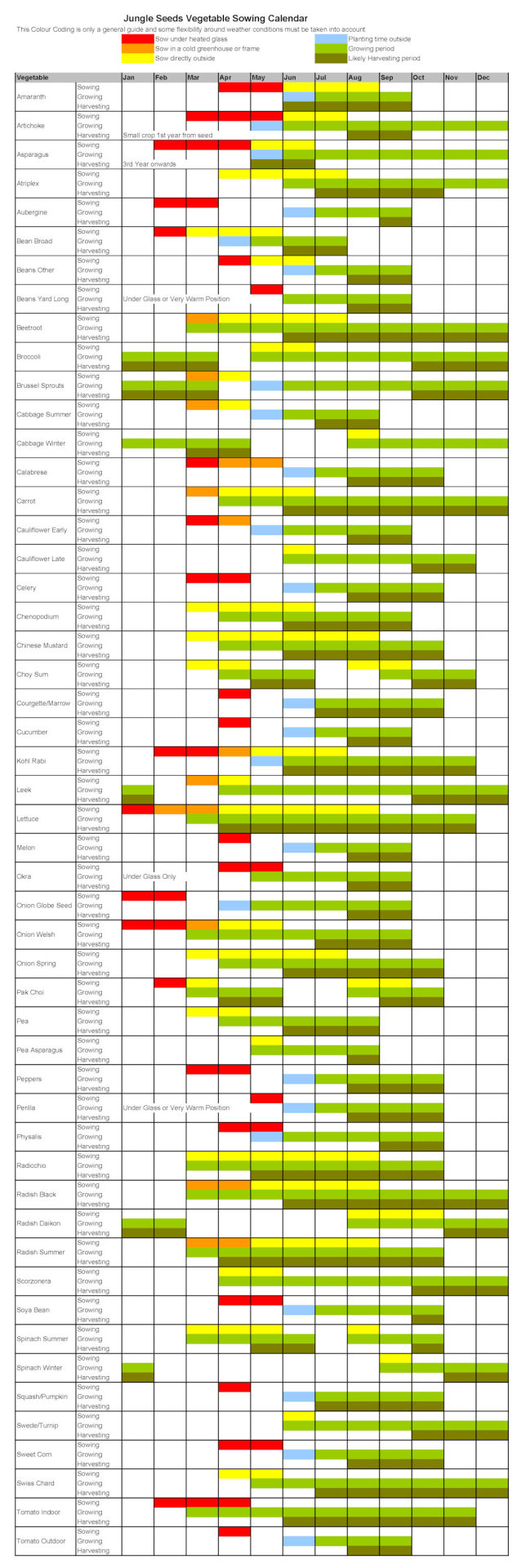
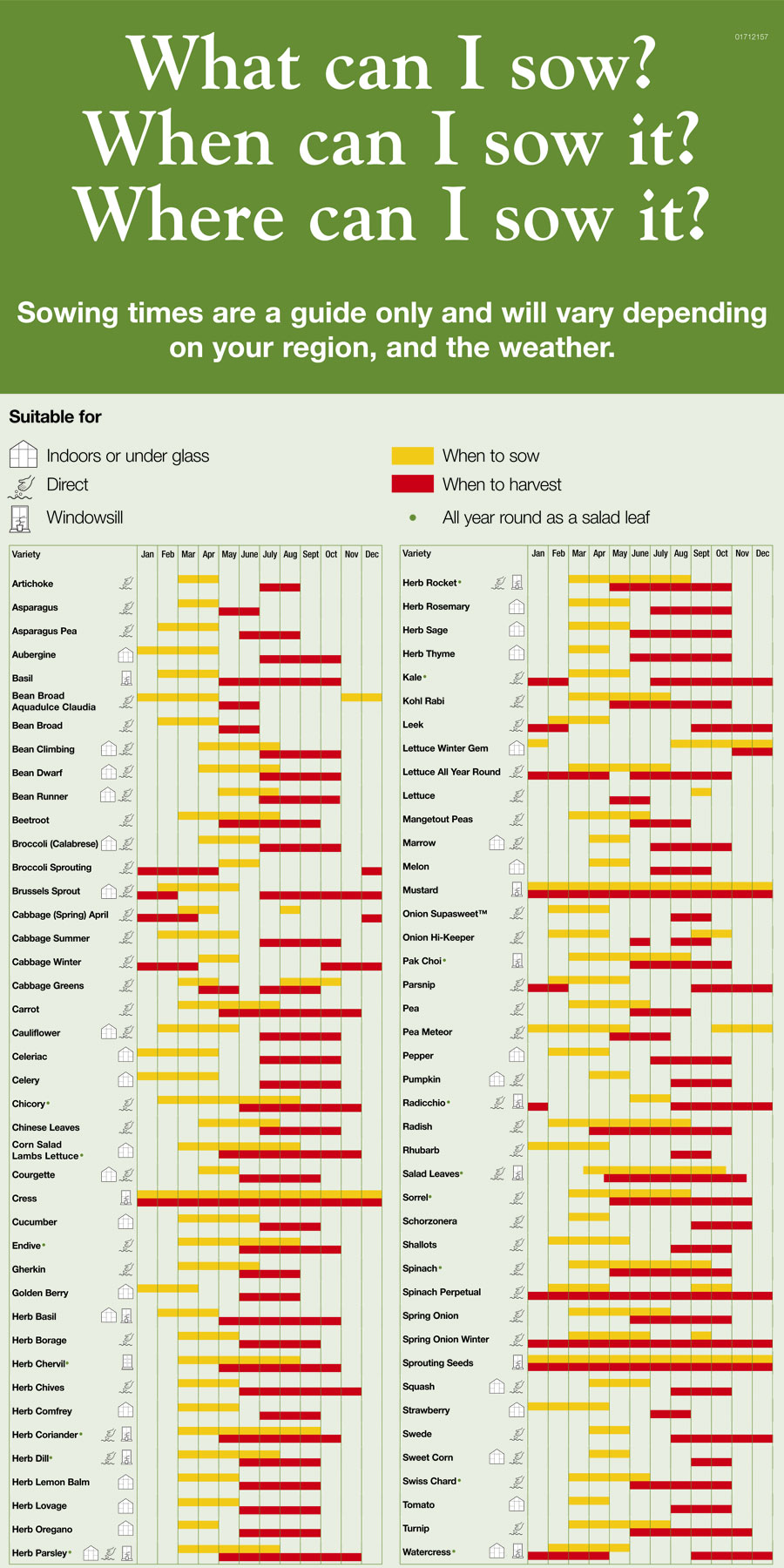
The Zone 6 Winter Sowing Calendar:
This calendar is a tenet; regulate it based mostly in your particular microclimate and the anticipated climate patterns to your area. Do not forget that germination occasions fluctuate between species.
October – November (Early Winter Sowing):
- Focus: Hardy annuals, biennials, and cold-hardy greens that profit from a interval of chilly stratification (a course of requiring chilly temperatures to interrupt seed dormancy).
- Appropriate Seeds: Calendula, candy alyssum, poppies, larkspur, cornflower, carnations, dianthus, lettuce (sure varieties), spinach, kale, chard, and sure herbs like parsley and cilantro.
- Issues: These seeds can tolerate a freeze-thaw cycle and can seemingly germinate in early spring. Guarantee your containers are well-protected from extreme rain and wind.
November – December (Mid-Winter Sowing):
- Focus: Extra cold-hardy species that require an extended chilly stratification interval.
- Appropriate Seeds: Most of the above, plus some slower-germinating greens like broccoli, cauliflower, and cabbage. Think about together with some wildflowers native to your area.
- Issues: Heavier snowfall is extra seemingly. Guarantee your containers are adequately insulated to stop freezing and thawing cycles that would injury the seeds. Examine for moisture ranges often, including snow or water as wanted.
January – February (Late Winter Sowing):
- Focus: Species with shorter chilly stratification wants or those who germinate readily in cooler temperatures.
- Appropriate Seeds: Some fast-germinating flowers like bachelor’s buttons, and sure herbs. Think about including seeds of greens that favor cooler temperatures, like peas and radishes.
- Issues: This era typically sees the coldest temperatures. Monitor containers intently for ice buildup and regulate insulation as mandatory. Heavy snow cowl might be helpful because it acts as pure insulation.
March – April (Early Spring Sowing):
- Focus: Heat-season crops and flowers that do not require chilly stratification. That is typically the time so as to add seeds on to the containers that didn’t germinate earlier.
- Appropriate Seeds: Zinnias, cosmos, sunflowers, basil, beans, cucumbers, squash, and peppers. Nevertheless, these could profit from a little bit of safety from frost till the hazard has handed.
- Issues: Temperatures are rising, so monitor for moisture loss extra steadily. You would possibly have to water extra often because the soil dries out sooner. Look ahead to early germination and be ready to skinny seedlings as wanted.
Container Choice and Preparation:
The success of winter sowing depends closely on choosing the proper containers. Recycled supplies are preferrred, selling sustainability and lowering prices. Listed here are some choices:
- Clear plastic containers: These are glorious for observing germination and monitoring moisture ranges. Milk jugs, soda bottles, and clear takeout containers work effectively.
- Different containers: You may also use yogurt containers, margarine tubs, or different meals containers, although clear plastic is mostly most popular.
- Drainage: Whereas glorious drainage is not important for winter sowing, some drainage holes are helpful to stop waterlogging, significantly in spring. A couple of small holes poked within the backside are enough.
- Lids: Lids or covers are essential to guard seeds from extreme rain and snow, whereas nonetheless permitting some air circulation. Use the unique lids or improvise with different supplies.
Sowing Combine:
A easy seed-starting combine is right. You do not want something fancy. A mixture of potting soil and vermiculite or perlite is really helpful. Keep away from utilizing backyard soil immediately as it could comprise weed seeds and illnesses.
The Sowing Course of:
- Put together the containers: Clear and put together your containers, making drainage holes if desired.
- Fill with combine: Fill the containers along with your seed-starting combine, leaving about an inch of area from the highest.
- Sow the seeds: Sow seeds in keeping with the directions on the seed packet. Typically, you need not bury seeds very deeply for winter sowing.
- Label the containers: Clearly label every container with the seed sort and sowing date.
- Safe the lids: Safe the lids or covers loosely to permit for air circulation.
- Place outdoor: Place the containers in a protected location, ideally sheltered from sturdy winds and direct daylight.
Monitoring and Upkeep:
- Moisture: Examine moisture ranges often, particularly throughout dry spells. Add water or snow as wanted, avoiding overwatering.
- Air flow: On hotter days, barely open the lids to extend air flow and stop fungal development.
- Pest and Illness Management: Winter sowing typically minimizes pest and illness issues, however monitor for any indicators of points.
- Seedling Thinning: As soon as seedlings emerge, skinny them to offer every plant sufficient area to develop.
Troubleshooting:
- Seeds not germinating: This may very well be on account of a number of components, together with incorrect sowing depth, poor seed high quality, or excessively chilly temperatures.
- Seedlings damping off: This fungal illness can happen if the soil is just too moist. Enhance air flow and guarantee correct drainage.
- Pest injury: Whereas much less frequent in winter, monitor for slugs and snails, significantly in spring.
Winter sowing in Zone 6 is a rewarding expertise. By following this calendar and the ideas supplied, you may efficiently begin all kinds of vegetation outdoor, saving time and assets whereas having fun with the satisfaction of watching nature nurture your seeds into wholesome seedlings. Keep in mind to adapt this calendar to your particular microclimate and climate circumstances for optimum outcomes. Glad winter sowing!





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied useful insights into Winter Sowing in Zone 6: A Complete Calendar and Information. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!